Ageing is a complex biological process influenced by both genetic and environmental factors and characterised by the gradual decline of numerous physiological and molecular functions. Recent findings highlight that epigenetic alterations are an important hallmark of ageing as they play key roles in integrating environmental signals to regulate gene expression and downstream cellular processes. In fact, it has been established that DNA methylation patterns serve as precise age indicators. Notably, the gene ELOVL2 has gained considerable attention as an aging biomarker, offering valuable insights into the phenomenon.
The ELOVL2 Gene: A Brief Overview & The Epigenetic Link
The ELOVL2 gene functions as a master regulator of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) synthesis. PUFAs are critical for numerous biological processes, and it has been reported that the PUFAs concentration in the body negatively correlates with age. ELOVL2 exhibits the strongest correlation with aging. One study show that ELOVL2 DNA methylation status explains 70% of the “ageing epigenetic clock”.
Moreover, some of the PUFAs under ELOVL2 control are abundantly present in the retina, where they promote healthy retinal function and have been linked to improving various vision conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration or even diabetic eye disease. ELOVL2 biomarkers are crucial for identifying the risk and status of age-related diseases.
Numerous DNA methylation based biomarkers (CpG sites) have been used to develop prediction age models, since their methylation status strongly correlates to chronological age similarly in all individuals. This can offer insights into an individual’s biological age and can serve as a “tracker” of quality of lifestyle and disease risk relative to chronological age.
In the case of ELOVL2, gene methylation tends to increase with age, leading to reduced gene expression. This change in gene expression is closely linked to numerous age-related processes and diseases, including skin ageing.
ELOVL2 and Skin Ageing
ELOVL2 is an important gene for determining longevity outcomes. It is widely researched that the level of ELOVL2 gene methylation patterns increase with age, which leads to a reduced expression. This shift in gene expression is believed to contribute to several age-related processes and diseases, including skin ageing, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular conditions. Researchers have been using ELOVL2 as an ageing biomarker and have included its methylation patterns in epigenetic clocks to study the ageing process and estimate an individual’s biological age.
Furthermore, ELOVL2 gene is vital for PUFA synthesis and as a result it plays a key part in the context of skin health. PUFAs are indispensable for maintaining the skin’s lipid barrier, preventing moisture loss and shielding the skin from environmental stressors. ELOVL2 downregulation results in a reduction of PUFAs which, in its turn, impacts the skin lipid composition, thus leading to dryness and compromised skin barrier function. Visible signs of skin ageing, such as the development of wrinkles and diminished skin elasticity, have been demonstrated to have a close link to decreased ELOVL2 methylation. Separately, another study showed this in dermal fibroblast from forearm.
Mitra Bio on ELOVL2
Mitra Bio is dedicated to leveraging genomics to increase lifespan and enable precision therapies for the skin – hence, we designed and developed a proprietary non-invasive skin sampling technique which, together with unique biomarkers, is used to track aging directly on human skin. ELOVL2 is one of the biomarkers used to measure how rejuvenation therapies affect the natural ageing processes within the skin. Lifestyle is the main driver of aging.
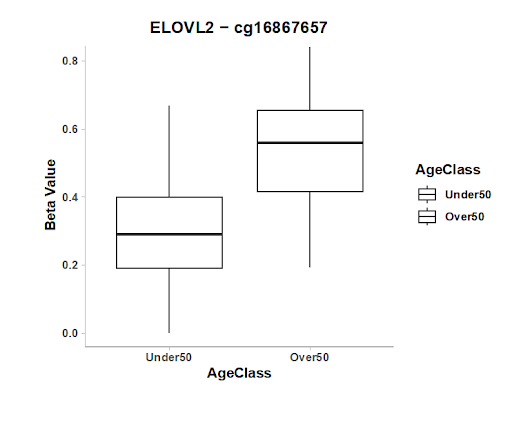
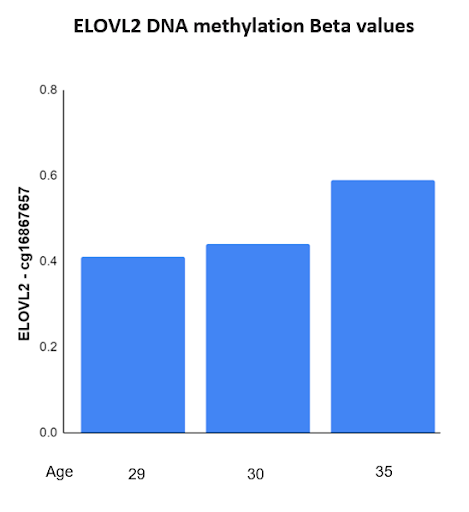
The importance of assessing and analysing skin biomarkers prior to initiating anti-ageing treatments needs to be emphasised, as it highlights the need to measure prior to intervention.
By assessing the CpG sites of the ELOVL2 gene, Mitra Bio aims to not only be able to measure age, but also delay or even reverse it.
Conclusion
The ELOVL2 gene has emerged as a fascinating player in the intricate field of aging research. Its involvement in fatty acid metabolism and its connection to numerous age-related conditions make it a promising target for future anti-ageing interventions. As our understanding of ELOVL2 deepens, it may hold the key to unlocking the secrets of aging and promoting healthier skin and more vibrant lives in our later years.
———————–
At Mitra Bio, we are using epigenomics to increase health-span and enable precision therapies for the skin. Mitra Bio has developed a proprietary skin sampling technique together with unique epigenetic biomarkers to track skin aging directly on human skin (replacing invasive biopsies, artificial skin or animal models). With a combination of clinical trials, non-invasive skin sampling, next-generation sequencing and state-of-the-art data science, Mitra guides the design of novel skin therapeutics that work directly on the human skin.
———————–


