Epigenetic changes refer to modifications that occur in gene expression patterns without altering the underlying DNA sequence. These changes can be influenced by environmental factors, lifestyle, and aging. One significant epigenetic modification is DNA methylation, which involves the addition of a methyl group to a DNA molecule, often occurring at specific sites called CpG sites. Change in the DNA methylation alter gene expression, and specific patterns can serve as biomarkers for tissue ageing and health.
As skin ages, there are characteristic changes in DNA methylation patterns. These changes are influenced by factors like UV exposure, oxidative stress, and inflammation. By analyzing DNA methylation patterns in specific genes related to skin health, one can gain insights into the biological age of the skin and its overall quality. This information can provide valuable data about skin aging, potential damage due to environmental factors, and even predict the efficacy of skincare interventions.
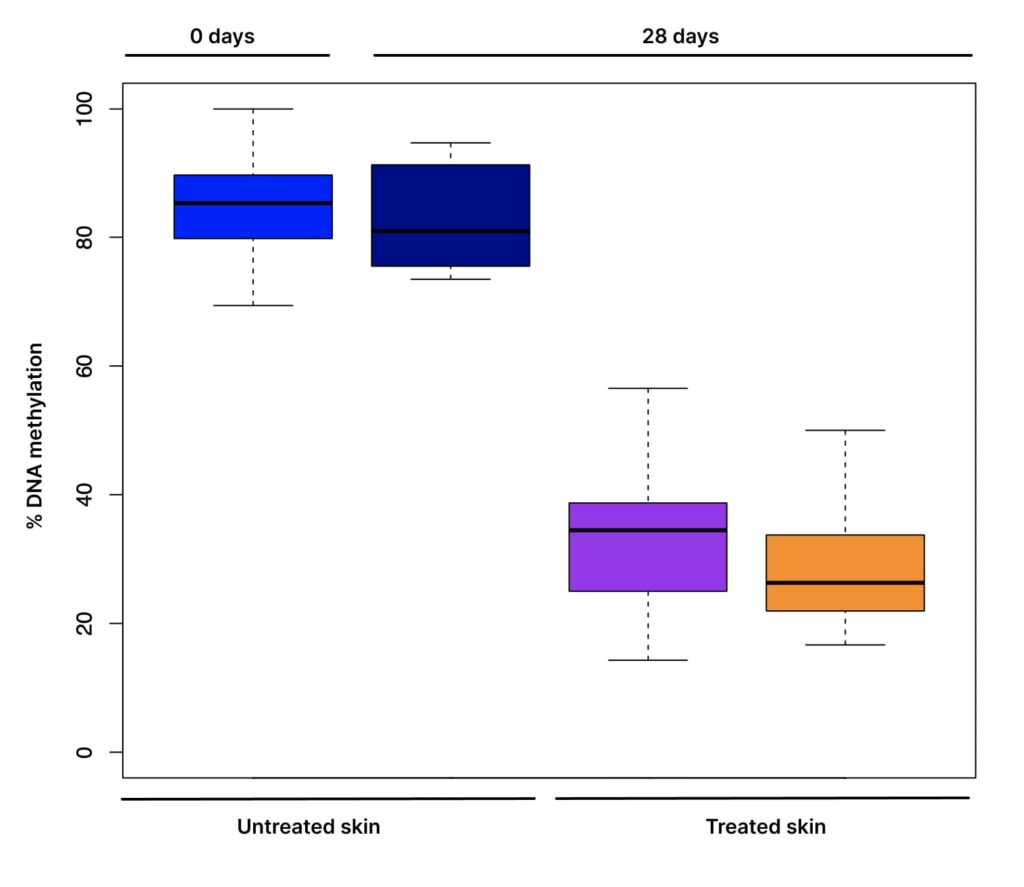
In a collaborative effort, Mitra Bio and Avon organised a 28-day clinical trial to explore DNA methylation patterns of the skin. The trial aimed to assess the effects of a topical cream enriched with the active ingredient, Protinol. During this period, the volunteers diligently applied the cream to the sides of their faces, while the forehead remained untreated. To gauge the outcomes, a novel approach was employed – Mitra Bio’s proprietary non-invasive skin collection method, utilizing tape-stripping, was employed for pre- and post-trial measurements. This innovative technique allowed for comprehensive insights into in-vivo epigenetic changes, all without the need for invasive biopsy procedures.
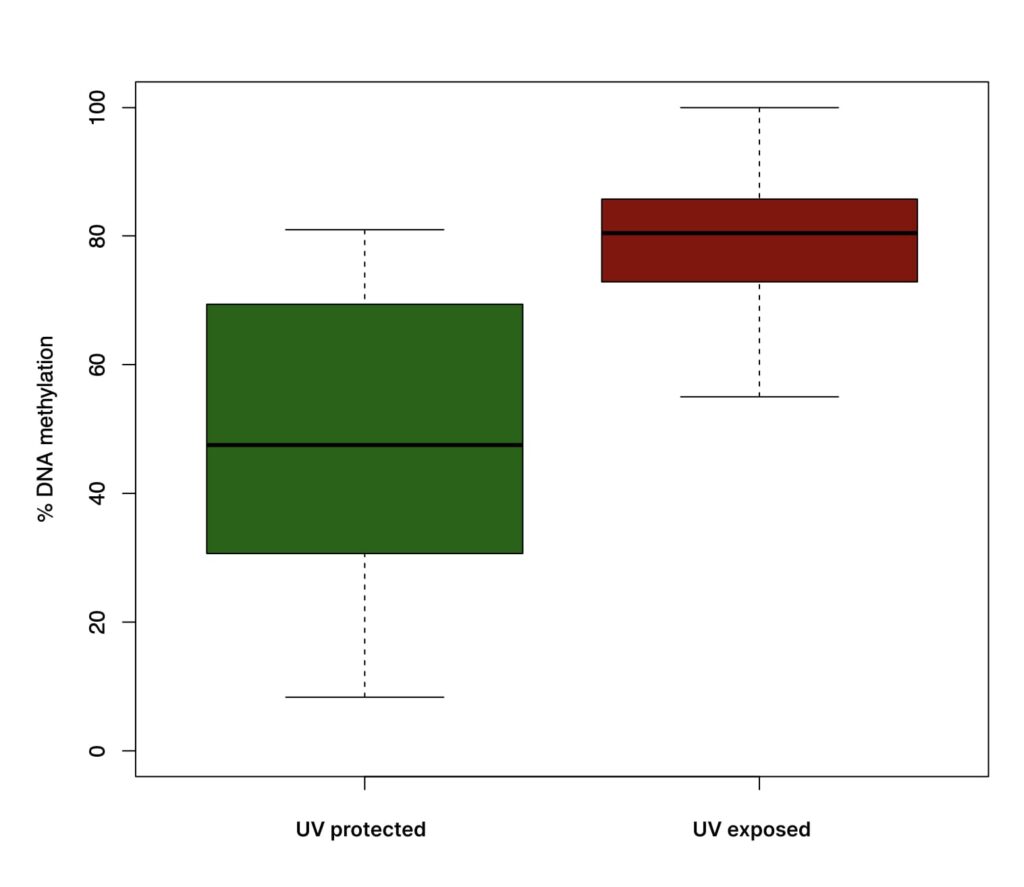
The results of the trial showed that using Avon’s Protinol had a direct impact on reversing the signs of UV damage, a major contributing factor to skin aging.
Marking a significant milestone, this study marked the debut of in-vivo epigenetic profiling of the skin, both pre- and post-application of a specific facial ingredient. This data was juxtaposed with Mitra Bio’s exclusive markers, derived from an internal trial focused on characterizing aged or sun-damaged skin. The findings unveiled an astounding 60 percent reversal in markers linked to sun damage within the treated areas after the 28-day period. These results stand as a compelling validation of the potential of small changes in prolonging skin health and proved that efficacious skincare products and sunscreens possess the capacity to enhance and even reverse the cumulative damage that accrues over time.
Mitra Bio conducted an analysis of DNA methylation profiling pre- and post- treatment. The significant CpG sites affected by the treatment were correlated with Mitra Bio’s earlier studied biomarkers. These notable changes were linked to the impact of UV damage due to sun exposure.
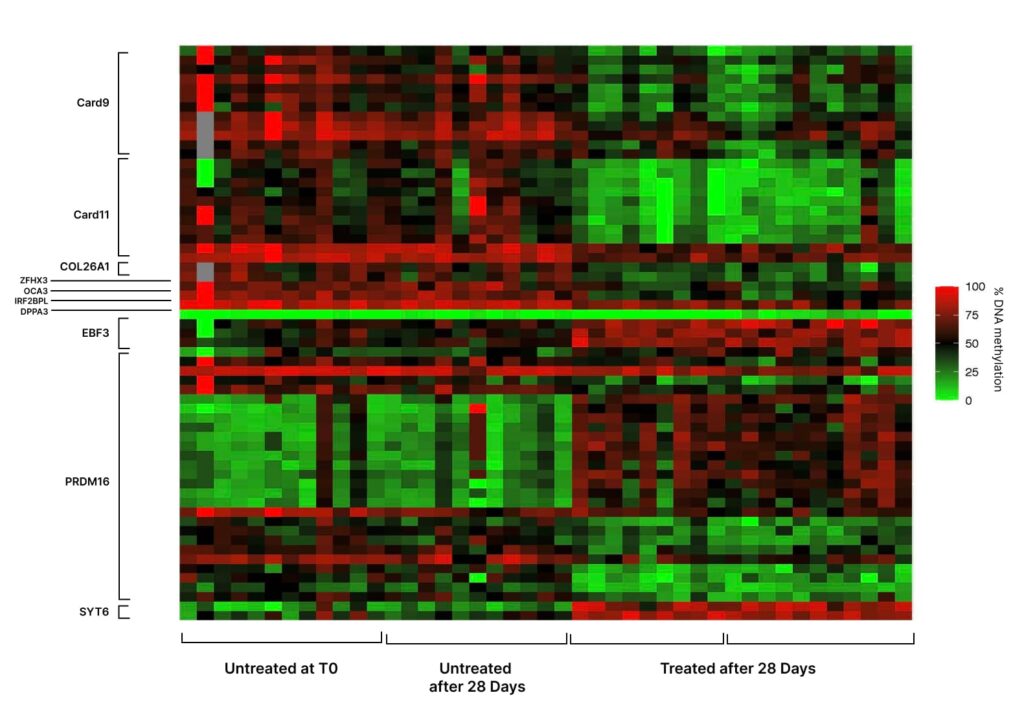
In addition, Mitra Bio conducted an extensive analysis of the genes exhibiting the most substantial alterations in DNA methylation biomarkers upon the application of the topical formulation. The observed methylation shifts were observed in several key genes, including:
- CARD9/11 – Implicated in immune response and inflammation.
- COL26A1 – Associated with structural support.
- ZFHX3 – Involved in skin development and function.
- OCA3 – Essential for skin function and predictor of pigmentation.
- 5.IRF2BPPL – Plays a role in immune response regulation.
These findings shed light on the specific genetic factors influenced by the topical formulation, providing valuable insights into its potential impact on skin health and function.
Through the Mitra Bio platform, we can effectively chart the progression of methylation changes over time in response to various factors such as product application or environmental shifts like sun exposure, pollution, and even hormonal changes like menopause. These newly identified biomarkers offer fresh insights into how the environment influences the intricate biological transformations within the skin, all without the need for invasive procedures. It’s a breakthrough that allows us to uncover the impact of external factors on skin health without any need for surgical intervention.
In summary, the collaboration between Mitra Bio and Avon has provided new insights into how skincare works. Epigenetic changes, particularly DNA methylation, offer a uniquely sensitive biomarker to track skincare interventions and show rejuvenation abilities to objectively complement claims. Mitra Bio’s platform enables the tracking of methylation changes over time, offering a revolutionary way to understand how the environment influences skin biology, all without invasive procedures. This advancement promises a new era of personalized skincare that enhances skin health naturally.